CaviTAU- "Cavitations Transalveolar Ultrasound Examination"
The CaviTAU® medical ultrasound scanner, for the dental practice, localises soft spots in the jawbone - so-called cavitations or FDOKs (fatty degenerative osteonecrosis in the jawbone) - by means of a novel imaging procedure that is free of harmful X-rays.
The reliable diagnosis of the quality of the jawbone helps to ensure that:
- Implants can be securely and firmly anchored
- No silent inflammations are present that could trigger possible chronic diseases
Bone softening as in fatty degenerative osteonecrosis of the jawbone (FDOK) cannot be detected with certainty on X-rays.
The safe and reliable diagnosis of the quality of the jawbone is carried out by ultrasound measurement. Using this radiation-free measuring method, we are able to visibly show existing silent inflammations or softenings of the jawbone.
We use the radiation-free ultrasound measuring device CaviTAU® in our practice.
Please bring a recent X-ray (OPG) with you to the examination.
In the literature you will find more information under the term NICO. Scientifically more correct, however, is FDOK. In short: fat-degenerated osteonecroses with neuralgiform symptoms are NICOs.
Independently of this, in FDOKs or NICOs we find an overexpression of cytokines such as RANTES, which correlate with systemic diseases (for more information, see Treatments Dental-IQ-Biohealth: FDOK/NICO).
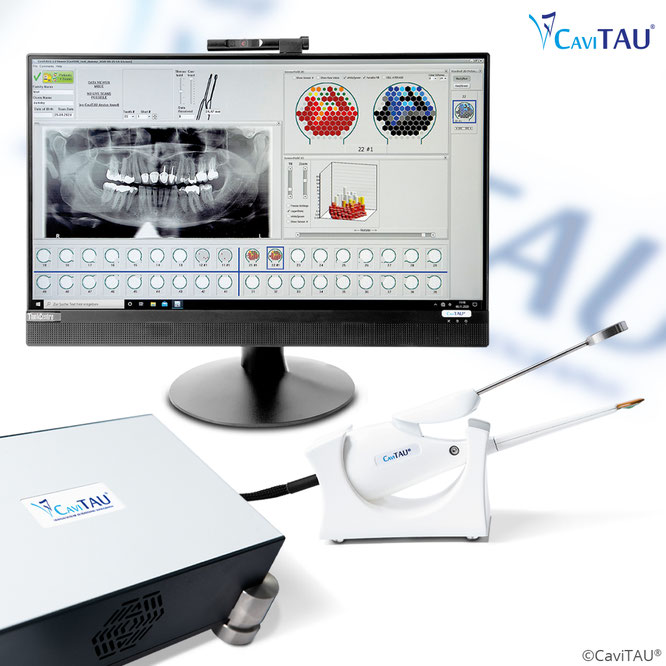
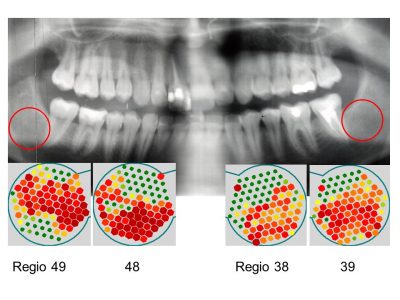
THE ULTRASOUND PROCEDURE SHOWS THE GRAPH OF BONE DENSITY.
Modern computer-assisted ultrasound technology thus enables the scientifically proven diagnosis of a degenerative-inflammatory jaw process:
Healthy and solid bone and tooth structures = GREEN.
Middle stage of chronic jaw ostitis = YELLOW/ORANGE
Fatty dissolved jawbone with bacteria and toxins = RED
To make the examination feasible, an aloe vera gel is used. In order to achieve a reliable diagnosis in men, it is of utmost importance that no beard is present. The ladies should come to the examination without make-up.
Have old extraction and surgical wounds (areas of former wisdom teeth), dead or root-treated teeth and dental implants examined with CaviTAU® in order to localise foci of inflammation quickly and without radiation. CaviTAU® offers both qualitative and operative advantages for dentists and patients.
Do you suffer from rheumatoid arthritis, trigeminal neuralgia or chronic fatigue?
(Contributory) causes can often be silent inflammations in the jawbone that are present but not noticeable by you.
We can detect these silent inflammations for you now. RADIATION-FREE. PREVENTIVE. FAST. INNOCENT. PAIN-FREE.
Your dental health is our passion.
CaviTAU® helps to locate foci of inflammation in your jawbone - thanks to ultrasound.
If you would like to learn more about CaviTAU®, please feel free to contact us at any time.
Figures - Data - Facts
Radiation protection, X-ray ordinance and TAU:
Another decisive aspect for the use of harmless ultrasound examination results from the X-ray Ordinance (RöV of 30.04.2003). The operation of X-ray equipment is strictly regulated by law because of the biological effect of ionising radiation (on DNA, chromosomes and the ability of each body cell to divide).
According to §15 of the Radiation Protection Act, the person responsible for radiation protection (in this case Dr. H. Knüppel) is responsible for ensuring that any exposure of people to radiation is avoided, and that any exposure of people to radiation is kept as low as possible, taking into account all circumstances of the individual case, even below the established limits.
The most important measure to ensure a radiation-hygienic procedure is the justifying indication. The "ALARA" principle ("aslowasreasonablyachievable") is the guiding principle here. It states that medical radiological diagnostics should be used in a way that offers a reasonable result with the lowest possible patient dose. Alternative procedures with lower exposure should be considered [1]. The effective dose of the three procedures panoramic tomography, DVT and computed tomography is approximately 1 : 10 : 100 [2, 3]. Finally, the application of this principle means that unnecessary examinations and duplicate examinations should be avoided as far as possible. Consequently, if no indications of osteopathy can be reliably detected even on a 3D DVT image, a computer tomography can be avoided with the help of TAU - if the anamnestic suspicion persists - which entails a hundredfold radiation exposure for the patient compared to a conventional 2D image. TAU measurement as a third imaging procedure has zero emission exposure compared to CT.
The completely non-invasive TAU ultrasound measurement is therefore suitable as a bone density measurement device to avoid further diagnostic radiation exposure (CT, scintigraphy, etc.) in the sense of §15. The rejection of non-exposure TAU ultrasound measurement on the part of payers and experts is thus tantamount to an indirect request to violate §15 of the Radiation Protection Act and hinders the avoidance of unnecessary bodily injury according to §15 of the Radiation Protection Act.
[1] Council Directive 97/43/Euratom of 30 June 1997, Official Journal L 180 of 09/07/1997:22-27.
[2] Ludlow JB, Ivanovic M: Comparative dosimetry of dental CBCT devices and 64-slice CT for oral and maxillofacial radiology. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral RadiolEndod 106, 106-114(2008).
[3] Schulze R: Radiation dose in radiological imaging for implantological problems in comparison: intraoral, panoramic slice, DVT and CT. Implantology 17, 377-386 (2009).
More : Figures - Data - Facts about CaviTAU
(Ultrasound versus X-ray)
Are there any scientific studies comparing TAU (Transition Alveolar Ultrasonography), ultrasound and X-ray?
Bouquot J, Martin W, Wrobleski G. Computer-based thru-transmission sonography (CTS) imaging of ischemic osteonecrosis of the jaws – a preliminary investigation of 6 cadaverjaws and 15 pain patients. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral RadiolEndod 2001; 92:550.
Bouquot JE, Shankland WE II, Margolis M. Through-transmission alveolar ultrasonography (TAU) – new technology for evaluation of bone density and desiccation. Comparison with radiology of 170 biopsied alveolar sites of osteoporotic and ischemic disease Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral RadiolEndod 2002; 93:
Wesley E. Shankland, II, D.D.S., M.S., Ph.D.: Medullary and Odontogenic Disease in the Painful Jaw: Clinicopathologic Review of 500 Consecutive Lesions. In: THE JOURNAL OF CRANIOMANDIBULAR PRACTICE OCTOBER 2002, VOL. 20, NO. 4, 295-303)
Bouquot JE, Shankland WE II, Margolis M, Glaros W, Through-transmission alveolar ultrasonography (TAU) – new technology for detection of Iow bone density of the jaws. Comparison with radiology for 92 osteoporotic alveolar sites with histopathologic confirmation. . Proceedings, annual meeting, American Academy of Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology, New Orleans, April, 2002.
Summary of these clinical studies:
"TAU was proven to be accurate at more that 99.99% in all cases totaling over 3,742 patients in peer reviewed studies. Comparing the TAU to X-Ray and enhanced MRI, the TAU was more than 2 times as accurate than the MRI and 3 times more accurate than X-ray."
